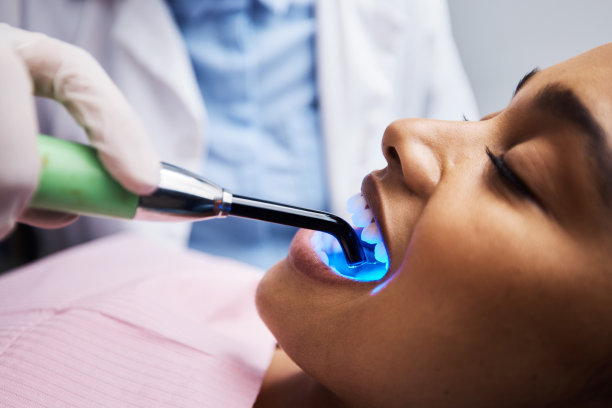
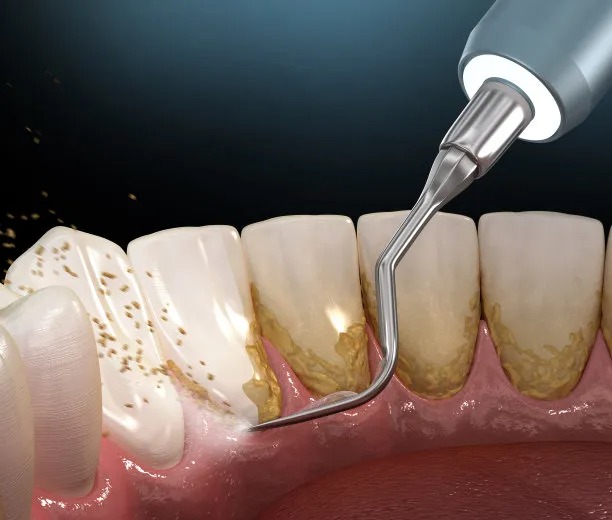
Summary: Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a prevalent oral health issue that can lead to significant health complications if left untreated. This article explores the causes of periodontal disease, including poor oral hygiene and genetic factors. It also highlights the effects of this disease on overall health, emphasizing its links to systemic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Furthermore, effective treatment options, from professional cleaning to surgical procedures, are discussed, offering insights into how individuals can improve their oral health and prevent periodontal disease. By understanding these aspects, readers can take proactive measures in maintaining their oral health.
1. Causes of Periodontal Disease Explained
Periodontal disease typically arises from the accumulation of plaque, a soft and sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. Poor oral hygiene habits, such as infrequent brushing and lack of flossing, lead to plaque buildup. When this plaque is not removed, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed professionally. The progression from gingivitis to more severe periodontal disease is significantly influenced by these habits.
Another important factor contributing to periodontal disease is genetics. Individuals with a family history of gum issues are more likely to develop the disease themselves. Genetic predisposition can affect how ones immune system responds to bacteria in the mouth, making some people more susceptible to severe periodontal complications than others.
Lastly, certain lifestyle choices can exacerbate the risk of developing periodontal disease. Smoking and tobacco use have been shown to impair gum health, as they interfere with blood flow to the gums, making it difficult for tissues to heal. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can increase vulnerability to inflammation and periodontal disease.
2. Effects of Periodontal Disease on Health
The effects of periodontal disease extend beyond oral health challenges. One significant link is its close association with systemic health conditions such as heart disease. Studies have shown that inflammation caused by periodontal disease can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular issues, underscoring the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene.
Furthermore, individuals with diabetes face a dual challenge, as periodontal disease can worsen blood sugar control. This interaction creates a vicious cycle; diabetes can increase the risk of infections, and periodontal disease can further complicate diabetes management. This reciprocal relationship highlights the necessity for comprehensive healthcare management for affected individuals.
A lesser-known effect of periodontal disease is its potential impact on mental health. Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to conditions such as stress, depression, and anxiety. The discomfort and aesthetic concerns related to periodontal disease can lead to social withdrawal and emotional distress, affecting overall quality of life.
3. Effective Treatment Options Available
Treatment for periodontal disease varies based on severity but often begins with professional dental cleaning. A dental hygienist removes plaque and tartar buildup, followed by a thorough assessment by a periodontist. Regular cleanings are vital to prevent the condition from progressing.
For more advanced cases, scaling and root planing may be required. This deep cleaning procedure involves scraping away plaque and smoothing the roots of teeth to remove bacteria under the gum line. It can help tissues to heal and reattach to teeth, effectively slowing the progression of the disease.
In severe instances, surgical options may be necessary. Procedures like flap surgery and bone grafts can help restore the supporting structures of the teeth. These interventions can significantly enhance oral health and quality of life for those affected, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional help when issues arise.
4. Importance of Preventative Care in Oral Health
Preventative care plays a crucial role in managing oral health and mitigating the risk of periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for detecting early signs of gum disease. A proactive approach can significantly hinder the progression of any dental issues, including periodontal conditions.
Additionally, maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine, including brushing at least twice a day and daily flossing, can help control plaque buildup. Using antiseptic mouthwash can provide an added layer of protection against bacteria and promote healthier gums.
Finally, educating oneself about the risks and symptoms of periodontal disease is vital for individuals and families. Awareness leads to early intervention and proper management, empowering individuals to take charge of their oral health proactively and effectively.
In conclusion, understanding periodontal disease, its causes, effects, and treatment options is imperative for maintaining oral health. By taking proactive steps to prevent and treat gum disease, individuals can significantly improve not only their oral health but also their overall well-being.
By presenting a comprehensive view of periodontal disease, this article emphasizes the importance of awareness and education in promoting better oral health practices. Empower yourself with knowledge and make dental health a priority for you and your family.
This article is compiled by Vickong Dental and the content is for reference only