Summary: Root canal treatment is a crucial dental procedure aimed at saving infected or damaged teeth. To ensure a safe and effective process, practitioners must adhere to essential guidelines and precautions. This article details four key aspects: thorough diagnosis and treatment planning, proper aseptic techniques, effective instrumentation and obturation methods, and post-treatment care. Each section elaborates on best practices, the importance of patient communication, and the need for follow-up to avoid complications. By understanding and implementing these guidelines, dental practitioners can enhance procedural outcomes, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care while minimizing risks.
1. Thorough Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
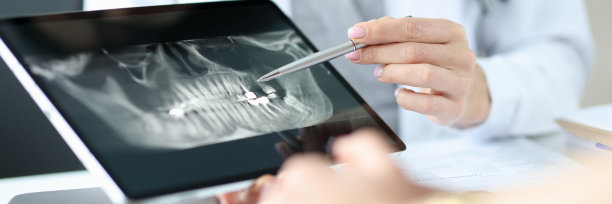
Before initiating any dental procedure, a precise diagnosis is paramount. Dentists must conduct comprehensive examinations, including radiographs, to identify the specific issues affecting the tooth. This allows practitioners to establish the most effective treatment plan tailored to the individual patient.
Having a clear understanding of the tooths anatomy, including the size and shape of the root canals, is essential. Advanced imaging techniques such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) can provide detailed insights into complex root canal systems, giving dentists the critical information needed for a successful procedure.
Moreover, effective communication with the patient is vital during this phase. Dental practitioners should explain the planned treatment, addressing any concerns while also ensuring that patients are aware of the associated risks and benefits. This transparency fosters trust and prepares patients for the upcoming procedure.
2. Proper Aseptic Techniques in Procedures
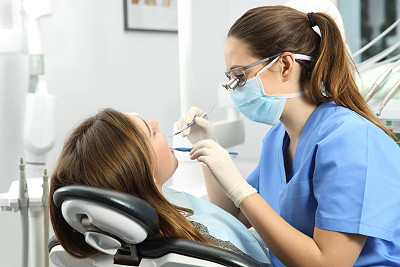
Aseptic technique is crucial in root canal treatment to prevent infection. Before starting the procedure, dental professionals must ensure that all instruments are properly sterilized. The dental unit and surroundings should also be free from microbes to minimize the risk of contamination.
Practitioners should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, masks, and goggles. This not only protects the practitioner but also safeguards the patient. Maintaining strict hygiene standards helps create a safe environment for the procedure.
Besides physical cleanliness, maintaining a sterile working field is critical. Utilizing a rubber dam during the procedure helps isolate the tooth and keep the treatment area clean, significantly reducing the chances of bacteria entering the root canal system.
3. Effective Instrumentation and Obturation Methods
Proper instrumentation is essential for cleaning and shaping the root canal system. Dental practitioners should use high-quality instruments that can efficiently remove infected tissue and debris while preserving the original tooth structure. This is crucial in achieving the desired outcome of the treatment.
The choice of obturation materials is also vital. Dentists should use biocompatible materials that provide a hermetic seal, preventing bacteria from re-entering the canal. Modern techniques, such as thermoplastic filling materials, can enhance the effectiveness of the obturation process, ensuring long-term success.
Additionally, regular assessments throughout the procedure are fundamental. Dentists should take radiographs at various stages to ensure that all canals have been adequately treated and filled, thereby minimizing the risk of complications later on.
4. Post-Treatment Care and Follow-Up
Post-treatment care plays a crucial role in the overall success of root canal therapy. Dentists should provide detailed instructions to patients about oral hygiene practices and recommend pain management options as needed. This helps ensure that patients recover swiftly and reduces the likelihood of complications.
Moreover, scheduling follow-up appointments is essential for monitoring the healing process. During these visits, practitioners can assess the treated tooth’s condition and identify any potential issues early on, allowing for timely interventions if necessary.
Establishing an open line of communication with patients encourages them to report any unusual symptoms, ensuring that complications are addressed as soon as they arise. This proactive approach to patient engagement is vital in enhancing treatment outcomes.
Summary:
In summary, effective root canal treatment hinges on thorough diagnosis and treatment planning, stringent aseptic techniques, efficient instrumentation and obturation methods, and meticulous post-treatment care. By adhering to these essential guidelines, practitioners can significantly reduce complications and enhance the overall patient experience.
This article is compiled by Vickong Dental and the content is for reference only.